PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
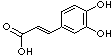
c1(cc(c(cc1)O)O)/C=C/C(=O)O
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
A natural dietary phenolic compound found in plants that is an anti-oxidant. Inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes that are involved in immunoregulation, inflammation and allergy. Inhibits Cu2+-induced LDL oxidation.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Caffeic acid
PubChem Compound Summary - Caffeic acid
IPCS INCHEM - Caffeic acid
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Caffeic acid
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Caffeic acid
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Caffeic acid
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - Caffeic acid
http://www.wisegeek.com/
Even though caffeic acid can be found in coffee, it is unrelated to caffeine. Together with its derivative caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), caffeic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound that is the product of many plants, including coffee beans. Caffeic acid is an antioxidant and it can also act as a carcinogenic inhibitor. Antioxidants, including caffeic acid, are essential in preventing diseases such as cancer or coronaries. Antioxidants consist of a molecule that is able to slow or even prevent oxidation of other molecules. When oxidation occurs in the body, it produces free radicals that are capable of damaging cells. Antioxidants terminate this reaction by removing free radicals that can be encouraged by smoking, stress, infections eating fried foods, excessive sunbathing, or exposure to pollution and x-rays. When the body has low levels of antioxidants, damage or death to cells can happen via a process called oxidative stress. This stress is a known contributor to the onset of many diseases, however it is not 100 percent understood whether it is the cause or the consequence of disease. The most common diseases are strokes and degenerative diseases. Caffeic acid also inhibits carcinogens. Carcinogens refer to any substances or agents that are involved in the promotion of cancer. There are any number of substances that can cause carcinogenic activity, but usually they are all related to the amount of radiation they emit.
Local:
Caffeic acid
is a non-nitrogenous acid found in various plants
as a metabolite product
in nature.
It is related to cinnamic
acid. But it has two
hydroxyl groups which is not found in cinnamic
acid. Caffeic acid
is not related to caffeine. Chlorogenic acid is
the ester of caffeic acid with the
3-hydroxyl group of quinic
acid. Caffeic acid is known as a naturally occuring phenolic acid which acts
as a carcinogenic inhibitor. It is also known as an
antioxidant in vitro and therefore
contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Caffeic acid and its
derivatives are used as
a component of antimitogenic, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflamatory, and
immunomodulator.
In
biological chemistry, cinnamic acid is a key intermediate in shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways.
Shikimic acid is
a precursor of many alkaloids, aromatic amino acids, and indole derivatives.
Phenylpropanoid are a class of plant metabolites based on phenylalanine. They are widely distributed in plants fulfilling many functions including plant
defense mechanism, pigmentation and external signaling
system. Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamates, coumarines, caffeic acids, ferulic acids, and sinapic
acids. Cinnamic acid is the precursor of
these acids. Cinnamic acid is
the parent compound of its esters which are more volatile
to
be transported to other parts easily.
Commercial cinnamic acid, a phenylacrylic acid structure
compound, is used in converting to its esters such as
methyl, ethyl, and benzyl cinnamate for the perfume and
flavour application. Cinnamic acid
and Its derivatives including esters and carboxylic functional derivatives
are used as important components in
flavours, perfumes, synthetic indigo and pharmaceuticals. Cinnamate can
act as optical filters or deactivate substrate molecules that have been excited
by light for the protection polymers and organic substances. They, cosmetic
grades, are used as sunscreen agents to reduce skin damage by blocking UV-A, B.
Cinnamic acid is an odorless white crystalline powder;
slightly soluble in water; melting point 133 C
and boiling point
300 C.
APPEARANCE
98.5% min
0.5% max
0.5% max
Not regulated
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Respiratory system, eyes, skin.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS


HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319-H335-H351-H361
P STATEMENTS
P261-P281-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
63-36/37/38-40-68
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36/37/39